Elecseed Sign Strategic MOU With Queensland Government And Korean Consortia
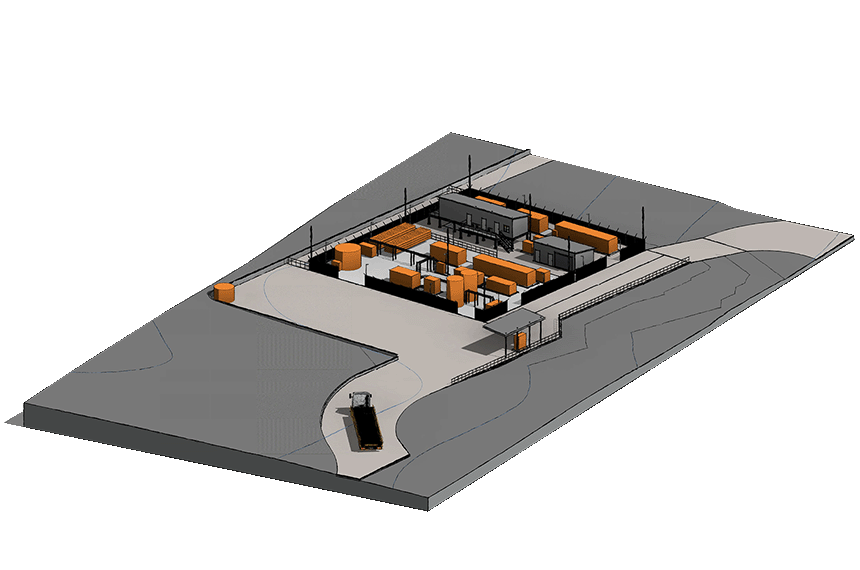
Elecseed, along with Korean consortia Shinhan Bank, LS-Electric, KOMIPO and IGIS Group have agreed a strategic MOU with the Queensland Government for the development of a pilot Hydrogen facility. The MOU was signed in Seoul on the 19th of September